
This article was updated on January 18th, 2024
As veterinarians, we often come across dogs with itchy skin or hair loss. These two symptoms combined can be caused by external factors such as parasites like fleas or mites, or internal conditions like skin infections or allergies. In this article, we will discuss the most common conditions that can cause both symptoms at the same time.
6 Common Causes of Hair Loss & Itching in Dogs [With Images]
There are several reasons that dogs will have hair loss and scratching. Some are simple conditions related to external circumstances like parasites or infections while others point to organ disease:
1. Flea infestation
Fleas on dogs can cause skin irritation and intense itching, but you may not always be able to see the fleas. If your dog develops a flea bite allergy to the pests’ saliva, the inflammation may lead to hair loss.
Pictures below: signs of flea infestations (hair loss, irritated skin, scabs)
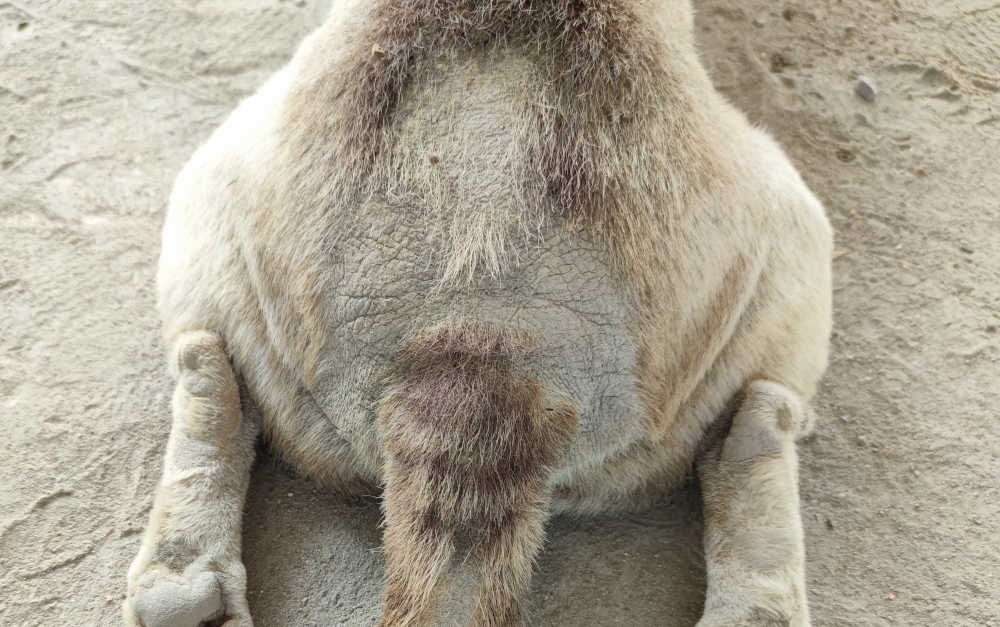
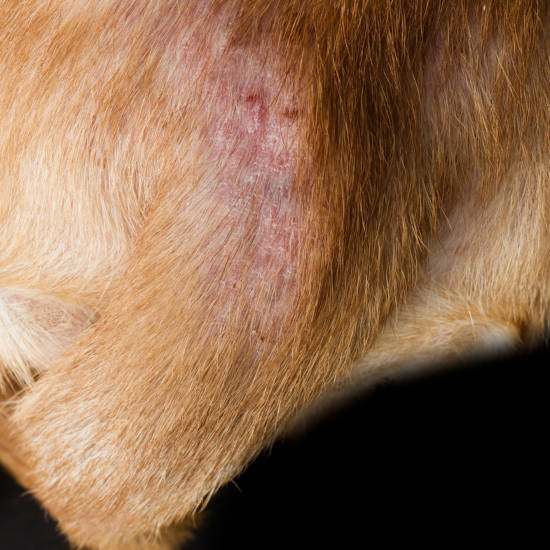
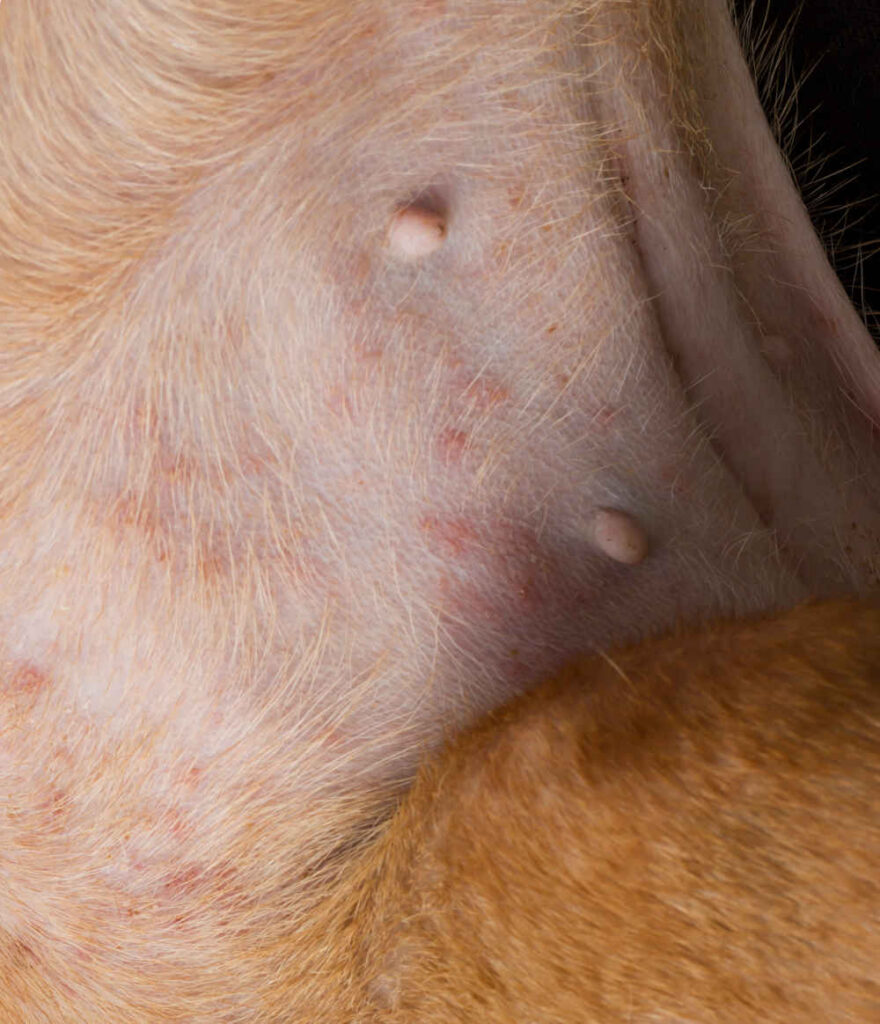
Signs of flea allergy dermatitis include:
- Biting at the tail or rear end
- Suddenly jumping up from a resting position
- Hair loss from the tail head up the middle of the back
- Open scabs from scratching/chewing
- Secondary skin infections
If you suspect your dog has fleas, treat him with a flea dip or shampoo and clean his bedding and environment. In the case of severe infestations or skin irritation, consult with your veterinarian about treatment options including flea control and anti-inflammatory medications if needed.
Learn more about flea allergy dermatitis.
2. Allergies
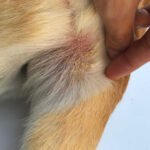
Allergies are very common in dogs. Allergies can cause itching, skin irritation, and hair loss (as well as other symptoms including ear infections, and gastrointestinal issues). Pictured below is a dog with skin allergies. Notice the red skin and trauma from repetitive itching.

Pictures below: allergies causing hair loss and irritated skin
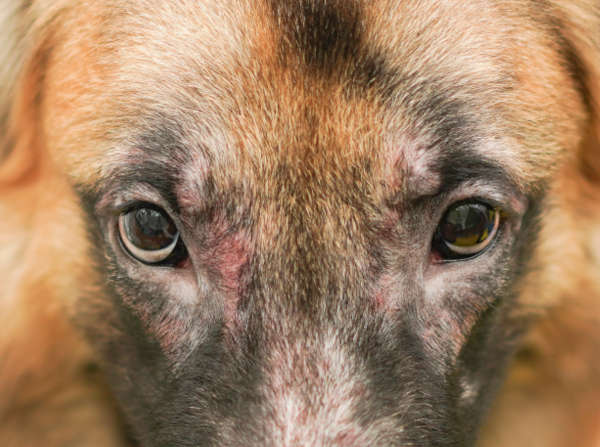
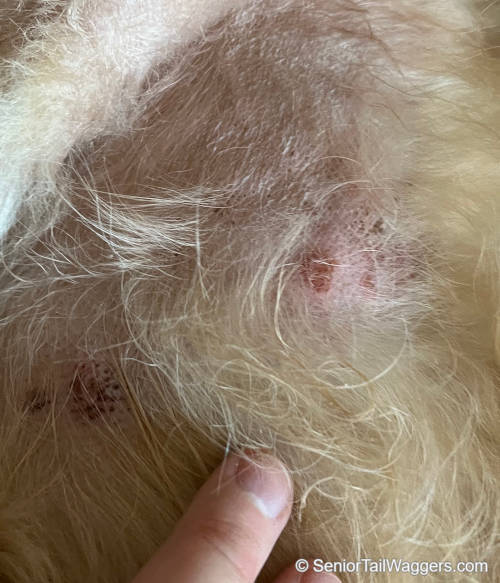


Certain foods, chemicals, and environmental stimuli can cause allergies in your dog. When the allergens trigger skin reactions, you may observe:
- Hair loss and poor hair coat
- Itchy skin – often around the paws and ears
- Licking the paws
- Chronic ear infections
- Red, inflamed skin
- Hives
The best way to manage your dog’s allergies is by identifying and avoiding the allergen. However, this can be tricky with dogs. If necessary, your veterinarian may prescribe antihistamines or other allergy relief medications to treat the symptoms. Once a dog shows sensitivity or an allergy to a stimulant, he will usually require lifelong management. Over time, the reaction may become more severe.
Learn more about skin issues due to allergies or hair loss due to allergies.
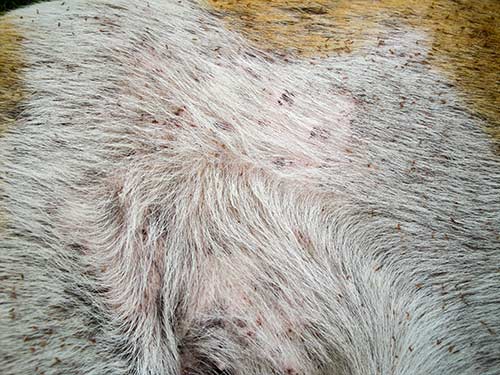
3. Mange (mites)
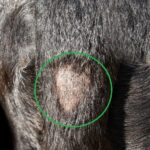
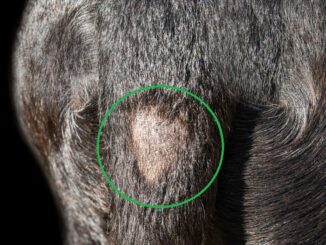
Mites are another skin parasite that can affect your dog and cause extreme itching with hair loss. When dogs have a mite infestation, certain species can cause scabies while others can cause mange. This dog on the picture below has mange and a secondary skin infection. Notice the bald spot and poor hair coat:
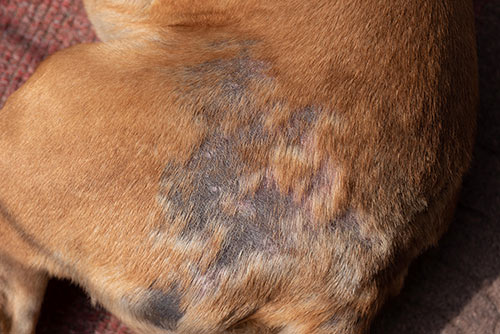
There are two types of mange in dogs: demodectic mange and sarcoptic mange (also known as scabies). Signs may include hair loss (in patches or generalized), itchy skin, crusty/red/swollen skin, pustules, and scabs. Note that sarcoptic mange is highly contagious among dogs, and these mites can also affect humans (it is imperative to thoroughly clean the environment to prevent recurrence or cross-infection).
Pictures of mange in dogs:
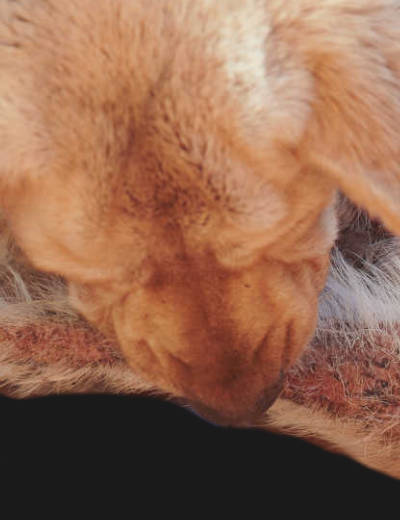
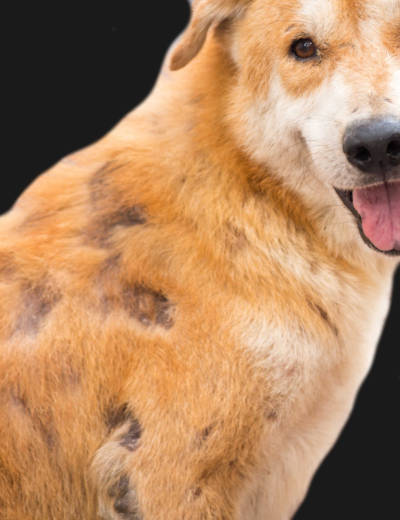
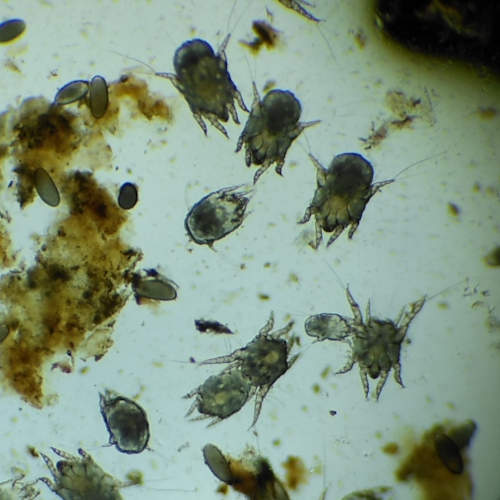



Learn more about Mange in Dogs
4. Skin infections
Bacteria like Staphylococcus spp and fungi like yeast or ringworm can cause skin infections in dogs. When these microorganisms affect your dog’s skin, you may notice:
- Itchy skin
- Redness and inflammation
- Pus or hot spots
- Skin crusting
- Circular hair loss
- Bumps or raised areas in the skin
- Changes in skin color
Pictures of skin infections in dogs (with hair loss and itchy, irritated skin):
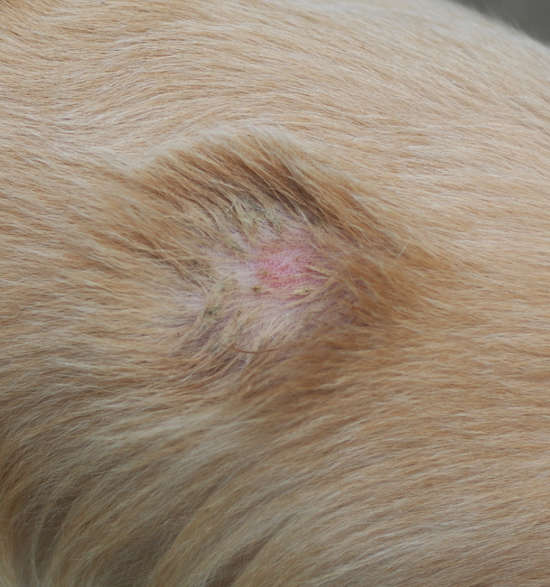
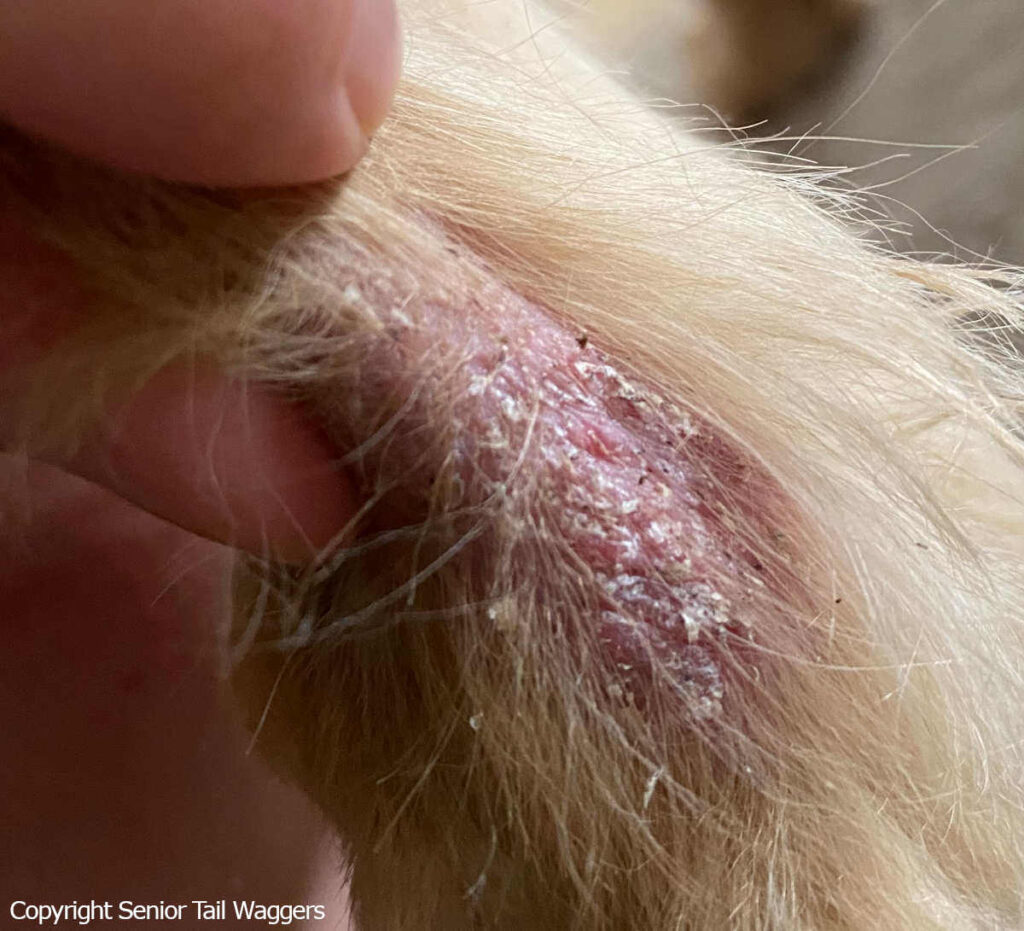
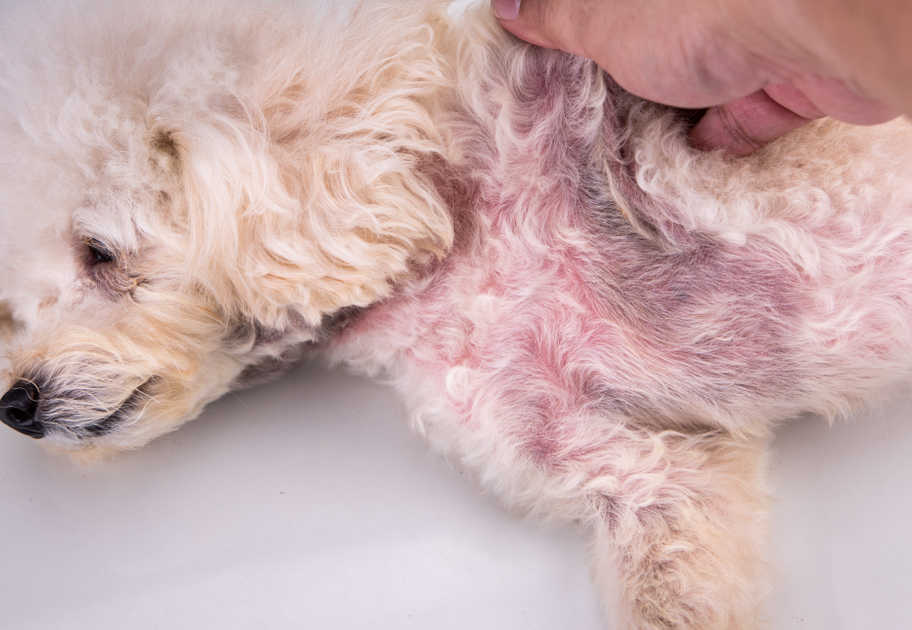
Treatment for skin infections varies depending on the causative factor. Your veterinarian will prescribe the appropriate antimicrobial drug. Additionally, you can use topical drugs, ointments, and medicated shampoos to help soothe irritated skin and promote healing. Some types of skin infections are difficult to cure and may take considerable time and attention.
5. Lice
Dogs can suffer from pediculosis, or a lice infestation. Fortunately, these crawling pests are species-specific, so they won’t transfer to you.
If your furbaby has pediculosis, you may observe:
- Adult lice which are tan, yellow, or medium brown and about the size of a sesame seed
- Vigorous scratching/intense itching
- Hair loss, often around the groin, rectal area, ears, neck, or shoulders
- A rough, matted coat
- Skin infections or small wounds from sucking lice
Lice are fairly rare in dogs, but they may be found on strays, feral dogs, and older or immune-compromised dogs. Treatment involves clipping off matted hair that may have attached eggs and adults and then using a veterinary-approved insecticide to kill the remaining pests.
The insecticide should be used repeatedly for a month or more to ensure all eggs and larvae that hatch are eliminated when they reach adulthood. You should also wash your dog’s bedding, collar, and any sweaters.
6. Hormone disorders
Dogs with hypothyroidism or Cushing’s disease can have hormone imbalances that cause hair loss and secondary skin infections that cause itching.
Hypothyroidism. If your dog suffers from hypothyroidism, you may notice:
- Hair loss/balding, dull, dry hair
- Susceptibility to ear and skin infections
- Dark pigmentation in the skin
- Lethargy, weight gain without a change in appetite
Hypothyroidism can be treated with thyroid replacement hormone, but the condition is incurable.
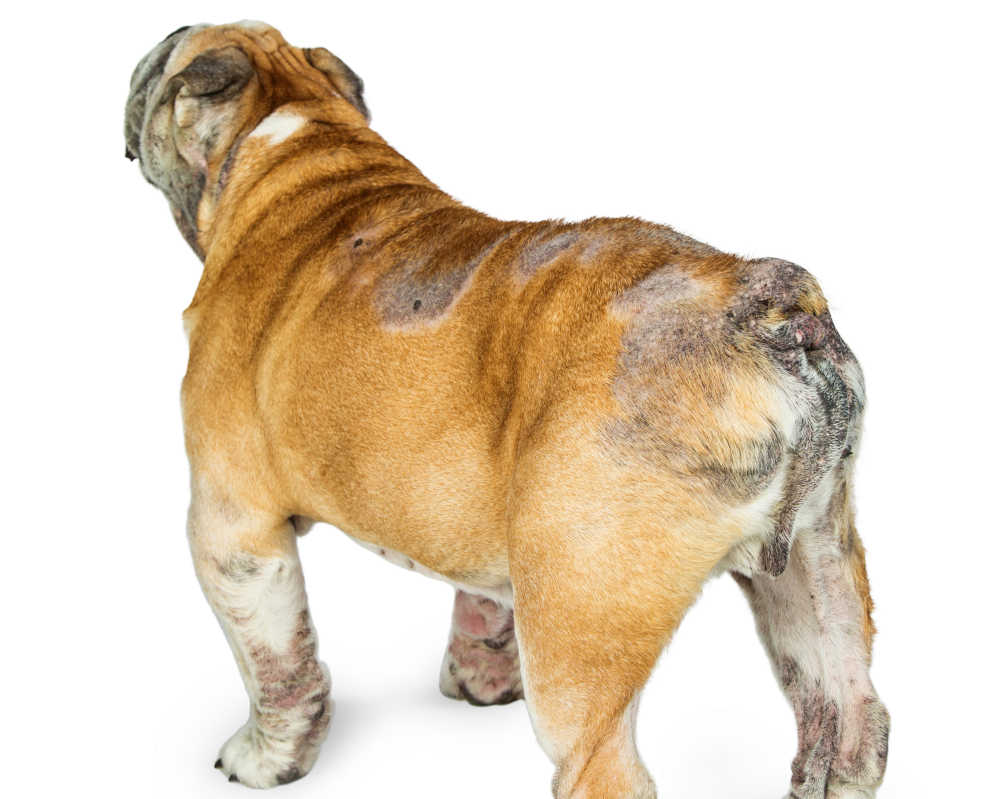
Cushing’s disease
Dogs with Cushing’s may exhibit the following signs:
- Thin skin
- Chronic skin infections that cause itching
- Symmetrical hair loss, as shown on the picture below
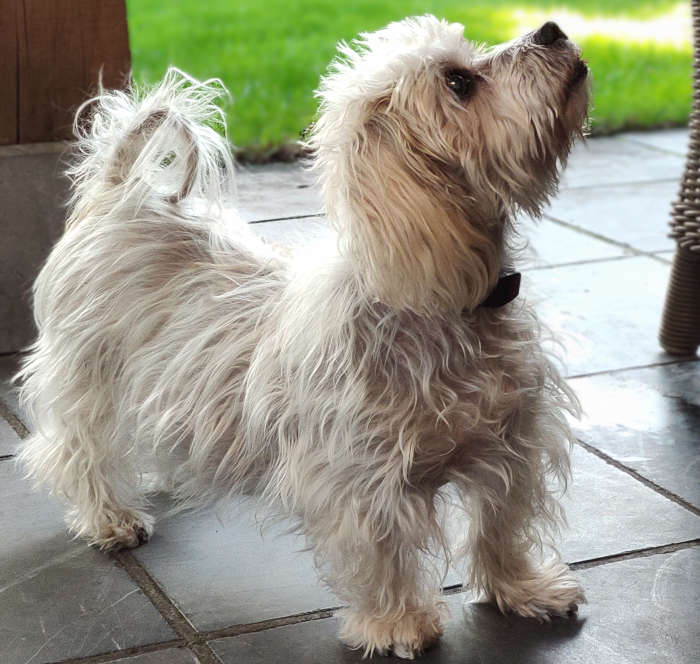

- Blackheads
- Pot-bellied appearance
- Lethargy
- Increased appetite
- Increased thirst and urination
Treatment will depend on the type of Cushing’s disease. Like hypothyroidism, Cushing’s disease can be managed but not cured. It will require lifelong monitoring and medical management. View more pictures of dogs with cushing’s disease.
Other symptoms to keep an eye on if your dog is itchy & losing hair
When hormonal problems, parasites, or environmental conditions affect your dog’s skin, it may have an inflammatory reaction. Dogs with inflamed, irritated skin frequently have the following symptoms:
- Inflamed, red skin that may also be bleeding
- Excessive chewing or scratching at areas of the skin
- Continually licking an area of skin
- Clumps of hair around the house
- Patches of bare skin or hair loss
- A red rash with bumps
If you observe combinations of these symptoms, you need to determine the underlying cause. Contact your veterinarian and report your observations. The sooner your doctor can reach a diagnosis and start recommended treatment, the sooner your furbaby will have some relief.
Can I wait to see if my dog improves, or should I call my vet?
If your dog has a combination of excessive itching and hair loss, you should contact your veterinarian:
1. Many of the conditions that cause these symptoms require veterinary treatment or medical management to provide relief for your furry friend.
2. Leaving irritated, itchy skin untreated can set your pooch up for more severe diseases. Continual licking or scratching an area may result in open sores that can become infected. Skin infections may get worse.
3. When you take a wait-and-see approach to your dog’s itchy skin and hair loss, you’re also prolonging your dog’s discomfort and impacting his quality of life.
4. Some of the causes of itchy skin with hair loss that we described above are contagious to other animals or humans. Waiting to see if your dog improves can put other family members at risk.
Home remedies are not always effective & usually fail to address the root cause
Home remedies are not always effective, and they may only treat the symptoms without correcting the underlying condition. If you’re trying any at-home approaches, contact your veterinarian immediately if you notice:
- Signs of an allergic reaction like hives, facial swelling, or respiratory distress
- Balding skin
- Changes in skin pigmentation
- A foul odor coming from the skin
- Pustules or crusty skin
- Changes in appetite
- Lethargy or depression
To diagnose the issue, your vet may run tests such as skin biopsies or scrapings
When you take your dog to the vet, he will start by asking you when you noticed the hair loss and itching, about his diet/supplements, if he’s on any medication, and if other family members are showing any symptoms.
After taking a history, the doctor will examine your dog and carefully examine the eyes, ears, and skin. Depending on his findings from the history and physical, the veterinarian will run tests to find a diagnosis. Testing may include:
- Bloodwork
- Urinalysis
- Skin scrapings
- Blacklight examination for ringworm
- Cytological examination of the skin
- Skin biopsies
- Fungal or bacterial cultures
- Hormonal testing
Frequently asked questions
Would a vet be able to help over a video call?
With a video consultation, the vet may be able to assess the severity of your dog’s condition. Unfortunately, many of the causes of itchy skin and hair loss share similar symptoms. On a video call, the veterinarian is not able to perform a complete physical examination or take diagnostic tests. Without a clear diagnosis, it’s difficult to develop an effective treatment plan to help your dog find relief.
How can I tell if my dog is “excessively” itchy?
Occasional scratching, chewing, or licking is normal behavior, so how will you know when it’s excessive? You need to know your dog and pay attention to his behavior. That way you can note any time he scratches, licks, chews, or rubs against objects more than usual. When you see changes in behavior, it’s time to talk to your veterinarian.
What are some common dietary deficiencies that cause hair loss?
Deficiencies in the following nutrients can lead to hair loss in dogs:
- Dietary protein
- Essential fatty acids
- Copper
- Zinc
Are there any home remedies for relieving itching in dogs?
You can try some of these home remedies to help your dog find relief. However, consult with your veterinarian before you use any at-home treatments.
- Feed your dog a bland diet if you suspect a food sensitivity
- Apply pet-safe(latex-free) aloe vera gel or spray to your dog’s itchy skin
- Make a 50/50 baking soda and water paste or a solution of 2 tablespoons dissolved in 1 cup of water to apply to itchy skin.
- Bathe your dog with 1 cup of finely ground colloidal oatmeal mixed with 6 cups of warm water
- Apply solid, unrefined/virgin coconut oil to itchy skin
- Steep 3 or more tea bags in a bathtub of water and soak your dog in the liquid when it’s lukewarm
- Make a 50/50 solution of apple cider vinegar and water that you can spray on your dog’s itchy skin
Related posts:
Disclaimer: This website's content is not a substitute for veterinary care. Always consult with your veterinarian for healthcare decisions. Read More.







Be the first to comment